Water table aquifers are usually closer to the earths surface than confined aquifers are and as such are impacted by drought conditions sooner than confined aquifers. A water table or unconfined aquifer is an aquifer whose upper water surface water table is at atmospheric pressure and thus is able to rise and fall.
If you are looking for water table unconfined aquifer you are coming to the right page. Everything Furniture contains many images about water table unconfined aquifer. Don't forget to bookmark this page for future reference and inspiration or share it on Facebook / Twitter and others if you like this page.

Protecting Drinking Water Aquifers Center For - View Full
The purpose of this study was to map the thickness and the configuration of the base of the unconfined aquifer in southeastern sussex county delaware figure 1.
Water table unconfined aquifer. See biscayne aquifer typically but not always the shallowest aquifer at a given location is unconfined meaning it does not have a confining layer an aquitard or aquiclude between it and the. 31 the amount of water stored can be related to the hydraulic head because both are proportional to the height of the water table. As opposed to a confined aquifer the water table in an unconfined aquifer system has no overlying impervious rock layer to separate it from the atmosphere. Unconfined aquifers are sometimes also called water table or phreatic aquifers because their upper boundary is the water table or phreatic surface. The water table and an aquifer are terms used when discussing groundwater. The unconfined aquifer provides much of the water used in this part of the state and is the first unit to be affected by pollution or waste disposal problems.
As water table height changes the hydraulic head is raised or lowered by the same amount. Unconfined aquifers are usually recharged by rain or streamwater infiltrating directly. In an unconfined aquifer as shown in fig. What you are looking at in this picture is a well that exposes the water table with an aquifer beneath it. The upper surface of this zone of saturation is called the water table. The groundwater below the confining layer is under pressure greater than atmospheric and if penetrated with a well the water level can rise above the top of the aquifer.
The depth to the water table varies according to factors such as the topography geology season and tidal effects and the quantities of water being pumped from the aquifer. The major difference between the two terms is that the water table references a specific portion of groundwater and an aquifer is all the groundwater present in the area. The upper groundwater surface in an unconfined aquifer is called the water table. A groundwater aquifer is said to be unconfined when its upper surface water table is open to the atmosphere through permeable material. For a groundwater reservoir to be classified as unconfined it must be shown that it is not confined by impermeable material relatively speaking and furthermore its water table cannot be confined from the effects of. The saturated zone beneath the water table is called an aquifer and aquifers are huge storehouses of water.
An aquifer in an unconfined state has entirely different storage properties than an aquifer in the confined or artesian state. Much of the public water supply in southern maryland and most of the delmarva peninsula including the eastern shore and delaware comes from confined aquifers.

Civ3248week4slides2019pdf Civ3248 Groundwater - View Full
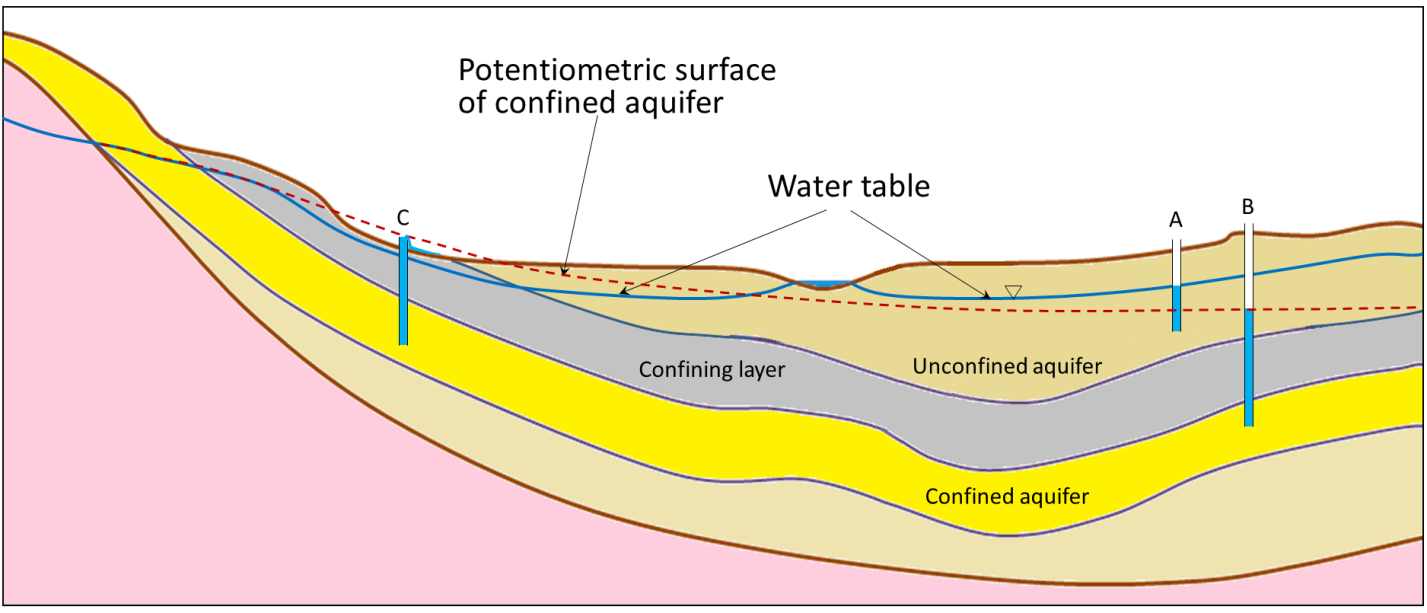
142 Groundwater Flow Physical Geology - View Full

Figure 2 From Groundwater Dynamics In Subterranean Estuaries - View Full

What Is The Relevance Of Confined Unconfined Aquifer Type - View Full

Adequate Image For Confined And Unconfined Aquifer - View Full







Post a Comment for "Water Table Unconfined Aquifer"